
Are you looking for a way to elevate your home’s comfort levels? The answer may be right under your nose. With the right heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system, you can maintain an ideal indoor temperature throughout the year. In addition, a well-optimized HVAC system can improve indoor air quality.
Understanding Your HVAC System
The HVAC system is a vitally important part of homes, offices, and nearly any enclosed space. By controlling indoor temperature, humidity level, and air quality, HVAC systems contribute to our comfort and health.
The Basics of an HVAC System
The fundamental purpose of an HVAC system is to provide heating and cooling to places, promote efficient energy use, and ensure that the air inside the building remains fresh. The goal of an HVAC system is to always maintain desired indoor conditions. This requires a complex interplay of components such as the furnace, air conditioner, and ductwork, working in harmony.
Key Parts of HVAC: Furnace, Air Conditioner, and Ductwork
The furnace contributes to the heating part of the HVAC system. It heats up air during the colder months, sending this warm air across other areas of the building. Secondly, the air conditioner, which consists of an outdoor unit and an indoor air handler, cools the warm air during the summer. And finally, the ductwork spreads the heated or cooled air throughout the premises.
Cost-Effective Ways to Boost HVAC Efficiency
In addition to performing their main functions, HVAC systems also help in energy conservation when used properly. Regular maintenance, scheduled service plans, upgrading appliances, and following energy-saving tips can substantially enhance the efficiency of your HVAC system with savings numbers depicted in lower energy bills.
Regular Maintenance
HVAC specialists suggest that regular check-ups and minor repairs like changing air filters can drastically increase the efficiency of HVAC systems. The main advantage of a regular service plan is that potential problems are detected early and rectified before they escalate. Furthermore, clean air filters facilitate smoother air flow and reduce the workload on the system, enhancing its lifespan while saving energy.
Upgrading Your HVAC System
If you’ve had your HVAC system for more than a decade, you might want to consider replacing it with a newer, more energy-efficient model. Central air conditioning, radiant heating, packaged systems, and heat pumps are all energy-efficient substitutes for older HVAC systems.
Energy-Saving Tips for HVAC Systems
In addition to regular maintenance and system upgrades, you can take some steps to improve the efficiency of your HVAC system. These include sealing and insulating your ducts, installing a programmable thermostat, and using your HVAC system more sparingly by utilizing fans and natural ventilation when possible.
Types Of HVAC Systems
There is an abundance of HVAC systems available on the market today. To help simplify your options, let’s explore each system and what it can offer.
Central Air Conditioners
Table of Contents
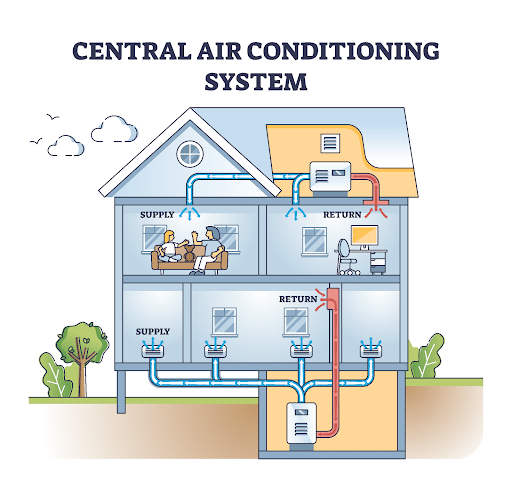
Of all the air conditioning systems available today, central air conditioning is one of the most efficient. For one, central ACs cover large areas and can be controlled collectively. They include an outdoor unit that combines the compressor and condenser, and an indoor air handler. The cooling process takes place when the air conditioner extracts heat from the air inside your home which is then expelled outdoors.
Single-Stage Heating and Cooling
Single-stage heating and cooling systems are efficient and easy to operate. They work on a simple mechanism of either on or off: when the temperature reaches a certain level, the system activates to provide heating or cooling. These systems are standard in many older homes but lack many of the intelligent features found in modern systems.
Multi-Stage or Modulating Heating and Cooling
These flexible systems adjust the amount of heating or cooling needed rather than simply being on or off. This can result in energy savings for homeowners. Modulating systems work more efficiently than their single-stage counterparts as they can alter their output depending on the indoor temperature.
Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats help you gain complete control over your HVAC system with intelligent features like sleep mode and the ability to program temperature changes throughout the day. They can be managed from your smartphone or tablet and can provide energy usage reports, alert system issues, and provide reminders for maintenance, such as changing air filters.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are an energy-efficient option for areas with mild heating and cooling needs. They work by transferring heat instead of generating it, making them cost-effective and environmentally friendly. There are three types: air-to-air (most common), water-source, and geothermal, all designed to heat or cool your home and provide hot water.
Furnaces
Furnaces are one of the oldest forms of heating and are still widely used today. A furnace works by heating air and distributing it throughout the house using ducts and vents. The power source could be gas, electricity, oil, or propane – choose the one that’s the most cost-effective in your area.
Boilers
Unlike furnaces that heat air, boilers heat water to provide heat. The hot water is pumped through pipes to radiators or underfloor heating systems. A boiler is ideal for creating a comfortable atmosphere during winter settings, especially when combined with a radiant heating system.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems

Mini split air conditioners are perfect for spaces where central air conditioning can’t reach or isn’t feasible. They provide exceptional energy efficiency, flexibility, and ease of installation. A ductless mini-split has two primary components: an outdoor condenser and an indoor unit that delivers cooled or heated air directly into the living space.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps use the stable underground temperature to both heat and cool your home. These pumps are considered some of the most efficient and environmentally friendly options on the market. Despite a higher initial investment, the savings on future energy bills can be significant.
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems offer the best of both worlds. Depending on the outdoor temperature, they can switch between a heat pump for milder temperatures and a gas furnace for colder periods. This efficiency makes them loved among homeowners who want to save on energy and enjoy a comfortable indoor climate.
Radiant Heating Systems
Radiant heating systems distribute heat directly to the floor or the panels on the wall or ceiling using infrared radiation. They provide heating slowly and evenly, providing warm comfort and eliminating cold spots. They come in either electric radiant underfloor heating systems or hydronic (liquid) systems.
Packaged Heating and Air Conditioning Systems
Packaged systems are perfect for homeowners with limited space. All the components – the compressor, condenser, and evaporator – are housed in a single unit, which is typically installed on the roof or a concrete slab. These systems are popular for their compact size and ease of installation.
Ventilation Systems
A key component of any HVAC system, ventilation systems work to maintain air quality within your home. They exchange stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air and help control humidity levels. Whether it’s an air exchanger or a simple window opening, ventilation is crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality.
Evaporative Coolers (Swamp Coolers)

Evaporative coolers, also known as swamp coolers, operate by evaporating water into the air. An effective solution in dry, hot climates, they work best when relative humidity is 60% or lower. In addition to cooling the air, swamp coolers also add humidity, making them a good choice for areas where air can get excessively dry.
Other Typical HVAC Components
In addition to heating and cooling units, a well-functioning HVAC system includes several other components. Air filters are crucial for maintaining indoor air quality, while silencers and vibration isolators ensure quiet operation.
Indoor Air Quality and HVAC
Maintaining good indoor air quality (IAQ) is more than just a comfort – it’s a health necessity. HVAC systems play a significant role in controlling the IAQ and comfort of your home. Here’s how:
The Importance of Indoor Air Quality

Indoor air quality is essential for maintaining good health. Poor IAQ can lead to health problems such as allergies, asthma, and other respiratory illnesses. It can also impact productivity and enjoyment of your home. Moreover, on a larger scale, good IAQ contributes to environmental sustainability.
How HVAC Systems Affect Indoor Air Quality
HVAC systems have a direct impact on IAQ. They control the amount of fresh air intake and humidity levels in your home. Regular maintenance and changing air filters can improve air quality and make your HVAC system more efficient. Also, using air purifiers and other IAQ products can further enhance the quality of your indoor air.
Tips to Improve Indoor Air Quality Using HVAC Systems
Regular maintenance can ensure that your system is working at peak efficiency. Changing your air filters every 3 months or according to the manufacturer’s instructions will help reduce indoor pollutants. Adding an air purifier or a humidifier can further improve your home’s IAQ.
Investing in the Right HVAC System for Maximum Comfort
Choosing the right HVAC system is more than just picking the most expensive or the one with the most features. It requires understanding your home, your budget, and your comfort preferences. For instance, while central AC and central air conditioning are the most common systems used for cooling, they may not be suitable for homes in cooler climates. Conversely, heat pumps and radiant heating systems might be better suited for such areas as they provide both heating and cooling.
Expected Costs and ROI for HVAC Systems
The cost of HVAC installation varies greatly based on the system type. For example, the average installation cost for a central AC unit is generally higher than a window air conditioner or a portable air conditioner. However, the initial cost doesn’t tell the whole story. It’s crucial to consider the operating cost, maintenance cost, and lifespan of the system as well. A higher initial cost might provide a better ROI in the long run if the system is energy-efficient and requires less maintenance.
Ready to explore your HVAC options? High Performance Home can help. We specialize in advising homeowners on the best products for their homes. Contact us today so we can help you find the right home components to make your space uniquely yours.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between HVAC and AC?
The main difference between HVAC and AC is that HVAC refers to full heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, while AC refers only to air conditioning.
How does a home HVAC system work?
A home HVAC system works by using components like furnaces, heat pumps, air conditioners, ductwork, thermostats, and vents to heat, cool, humidify, dehumidify, and circulate air throughout a home for thermal comfort and indoor air quality.
How often should I replace my HVAC system?
HVAC systems typically last 15-20 years. Schedule yearly maintenance to maximize lifespan.
